Tutors
Available 24/7
Accounting
Economics
Education
History
Marketing
Mathematics
Statistics
Writing
Services
Chapter 10 does not have Questions for Homework.
Economics Learning Center
is for students, teachers, and professionals.
Free Internet Libraries
improve grades and careers.
Free Stuff For Students
is an
extensive collection.
Please Visit Our Other
Free Internet Libraries
Index
Textbooks Libraries
Free Computer Libraries
Business Libraries
Mathematics Libraries
General Interest Libraries
Education
Special Interest Libraries Textbooks Libraries
Business Textbooks
Nonbusiness Textbooks
Quick Notes Course Outlines
Educational Audio Videos
Free Computer Libraries
Free Business Software
Free Software Tutorials
Excel Internet Library
Mathematics Libraries
Business Libraries
Accounting
Business Media
Criminal Justice
Economics
Investment
Leadership
Management
Marketing
MBA
Personal Finance
Small Business
Mathematics Libraries
Mathematics
Statistics
General Interest Libraries
Student Library
Online Books Library Education
Education Improvement
Educational Audio Videos
Special Interest Libraries
Dieters
Research Paper
Foreign Students
Please Visit our sponsors
Devry
University
Computer Speed Typing Made Easy
Mind Tools
has these essential skills to
enhance your career.
Learn Leadership Skills from the Experts
is a self-study leadership system with tools, tips, and email leadership
courses.
Make Time For Success
is a
self-study program with 39 tips from the pros on managing your time, effort,
and that of others.
Stress Management Masterclass
how you how to tackle the deep structural problems that cause stress in your
working life.
Free Internet Libraries
improve grades and careers.
Free Stuff For Students
is an
extensive collection.
File 8 Questions for homework
1. This analysis demonstrates how the inflation
of the late 1970's and early 1980's
caused a decrease in the standard of living
for the average person living in the
United States. Using the data below,
calculate a consumer price index, real
disposable personal income, nominal per
capita disposal personal income, and real
per capita disposable personal income.
Use 1981 as the base year. Round CPI to
whole numbers and others to thousands of
dollars. Data given represents actual
data for the period.
| Year
|
Cost of a Basket of Goods |
CPI |
DPI in Billions |
Real DPI |
Population |
Nominal/ |
Real/Capita DPI |
| 1978 | $400 | 72 | $1, 551 | $2,154 | 223 | $6,955 | $9, 659 |
| 1979 | 445 | 80 | 1,729 | 2,161 | 225 | 7,684 | 9,604 |
| 1980 | 505 | 91 | 1,918 | 2,108 | 228 | 8,412 | 9,246 |
| 1981 | 557 | 100 | 2,128 | 2,128 | 230 | 9,252 | 9,252 |
| 1982 | 592 | 106 | 2,261 | 2,133 | 232 | 9,746 | 9,194 |
| 1983 | 611 | 110 | 2,428 | 2,207 | 235 | 10,332 | 9,391 |
| 1984 | 637 | 114 | 2,669 | 2,341 | 237 | 11,262 | 9,878 |
2. Explain the economic ramifications of your answer to Question #1.
The data demonstrated how real disposable income stagnated during the period.
As
with any average, the extremes are not evident. In this case, the Midwest
was hit
hard and became known as the Rust Belt. New England and California
weren't hit as hard.
Chapter 9 Questions for homework
1. First, calculate two annual rates of inflation for a basket of goods that increased
in price from $600 to $630 and then to $693 over two years. Second, calculate the
inflation
rate over two years. Why was the inflationary rate over two years
exactly .5% higher than
the sum of the rate changes for each year?
(PL - PE)/PE = $630 - $600 = $30 = .05 = 5%
$600
$600
(PL - PE)/PE = $693 - $630 = $63 = .1 = 10%
$630 $630
(PL - PE)/PE = $693 - $600 = $93 = .155 = 15.5%
$600 $600
2. Calculate the total unemployment cost incurred by a 5
trillion dollar economy
of 250 million people during the 1990-92 recession and subsequent slow
recovery.
Assume the unemployment rate was up an average of 1.5% each year for the
three-
year period. What was the total cost to a family of four?
GNP change = 2.5 x Unemployment = (2.5)(1.5%) = 3.75%
annual absolute change = (3.75)(GNP) = (3.75%)($5 trillion) =
$187,500,000,000
annual per capita change = GDP change population
= $187,500,000,000 250,000,000 people = $750/person
annual cost to a family of 4 = (4)($750) = $3,000 and the three
year cost is $9,000
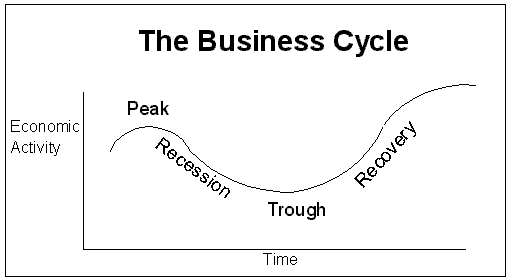
3. Contrast cost-push and demand-pull inflation.
Cost-push inflation is the result of a shortage in supply. It often accompanies
the end of the expansionary stage of the business cycle when resources become
scarce. Demand-pull inflation begins in the recovery stage of the business cycle
and continues to increase with expansion.
4. Who is helped and hurt by inflation? Give examples from your own experiences.
A. Debtors (homeowners, business, and government) are helped by moderate inflation.
The economic effects of the high inflation of the 1970's continue today. The US
struggles with the high cost COLA's, the end of tax bracket creep, high social
security payments, and other programs adopted because of high inflation.
B. Fixed income earners and creditors are hurt by inflation
Note: The high inflation in home prices on each coast helped the lucky owners
who sold at the right time and traded down but, it will
be many years before
those who bought high get back to even.
5. Define and give examples of the three types of unemployment.
A. Frictional unemployment is the result of time lags in the operation of the
labor market as people require time to find new jobs, careers, etc.
B. Structural unemployment is the result of changes in product demand and
technology.
Both the Rust Belt of the 1980's and New England's computer
industry of the early 1990's are good examples.
C. Cyclical unemployment is the result of a decrease in total economic activity.
An example is the recession of the early 1990's. Demand slowed for a number
of
reasons, not the least of which was the high structural unemployment of the
period.
Structural and cyclical unemployment began to feed on each other. As
a result, the
recession dragged on and the recovery was slower (weaker) than
average recoveries.
6. Draw and label a graph depicting the business cycle. (see figure 21 graph page 2)